Introduction
Companies often face challenges in developing diversity and inclusion in their supply chains. Many providers from underrepresented groups struggle to achieve equal opportunities due to systemic barriers. Supply chain diversity addresses this issue by actively engaging diverse suppliers such as small businesses, local vendors, social enterprises, and minority-owned enterprises.
This approach provides access to innovation, enhances ethical representation, generates positive publicity, and improves market adaptability. The article explores supply chain diversity, its concepts, challenges, implementation methods and benefits.
What is Supply Chain Diversity?
Supply chain diversity refers to the intentional involvement and active participation of various suppliers from diverse backgrounds, ownership structures, and business models in an organisation’s procurement and sourcing processes.
This includes actively seeking and providing similar opportunities for professions that have traditionally faced barriers or underrepresentation, such as:
- Small and micro enterprises
- Local vendors and suppliers
- Social enterprises or mission-driven businesses
- Companies owned and operated by underrepresented groups, including women, ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ individuals, people with disabilities, and others.
Principles for Supply Chain Diversity
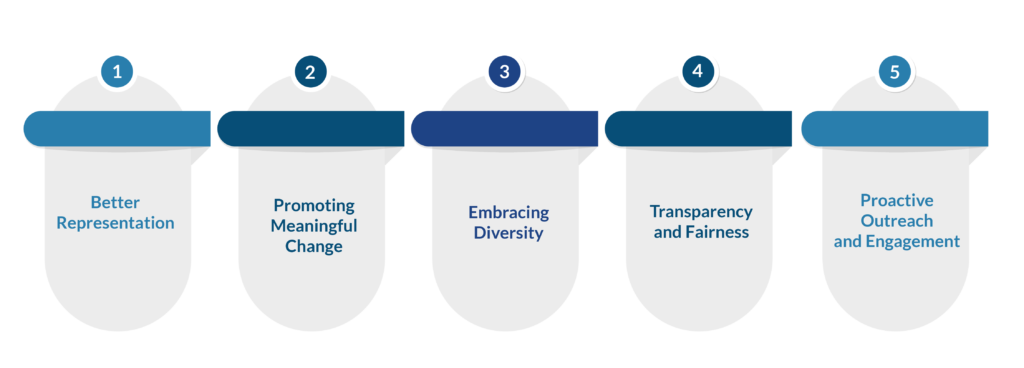
Enhancing diversity and inclusion is an important strategy that requires genuine engagement in equal opportunities, acceptance of different perspectives, and meaningful change. It is not just a box-ticking exercise but the belief that diversity opens up new possibilities, fosters growth and contributes to a more equitable society.
- Better representation: Equitable representation for underrepresented and minority-owned businesses in leadership, supply chain, and decision-making.
- Promoting Meaningful Change: Strategies that challenge systemic barriers and promote inclusion, equity and real change.
- Embracing Diversity: Championing diverse voices, ideas, and innovations from different backgrounds supports creativity, problem-solving, and competition.
- Transparency and fairness: building trust through clear processes, clear standards, open communication, and addressing biases.
- Proactive Outreach and Engagement: Actively identify, engage with and support underrepresented supply communities for equal opportunity and success.
By adopting these principles and integrating them into procurement and sourcing practices, organisations can unlock the potential of diverse suppliers, inspire innovation and contribute to a better business environment.
Implementing Supply Chain Diversity
- Develop a formal supplier diversity program outlining goals and strategies for engaging diverse suppliers, such as minority, women, veterans, LGBTQ+, and disability-owned businesses.
- Set clear, measurable goals for diverse supplier participation based on spend, number of suppliers, or percentage in specific categories.
- Collaborate with organisations supporting diverse business communities to identify and connect with potential diverse suppliers.
- Review procurement policies and practices to ensure inclusivity, eliminate bias, streamline bidding, provide equal access, and offer training/mentorship.
- Invest in capacity-building initiatives like training, mentorship, access to capital, and guidance for diverse suppliers.
- Implement robust tracking and reporting systems for diversity metrics like several diverse suppliers, spending, and performance.
Implementing these strategies fosters an inclusive supply chain, taps into new talent and innovation, drives growth, enhances competitiveness, and strengthens relationships with diverse stakeholders.
The Benefits of Supply Chain Diversity
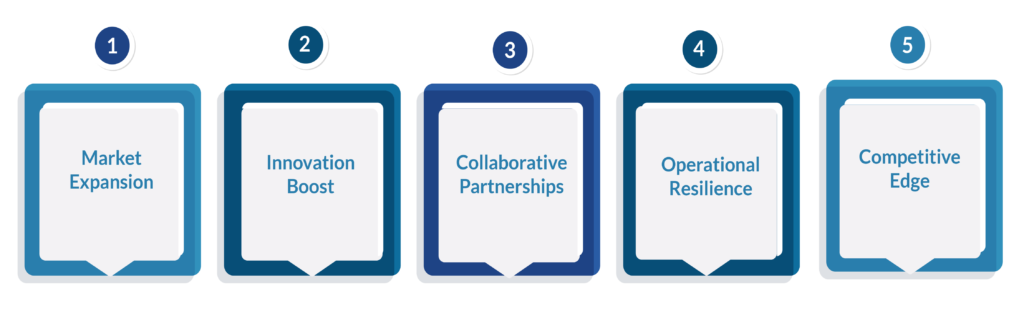
Here are the benefits of supply chain diversity in 5 points:
- Market Expansion – Access to new customer segments and insights into diverse communities, enabling tailored offerings and unlocking growth opportunities.
- Innovation Boost – Fresh perspectives and diverse viewpoints spark innovative ideas, solutions, and approaches to address evolving customer needs.
- Collaborative Partnerships – Improved supplier relationships, fostering mutual trust, effective communication, and joint efforts for continuous improvement.
- Operational Resilience – A diversified supplier base mitigates risks, increases flexibility, and enhances agility in adapting to disruptions and market changes.
- Competitive Edge – Differentiated offerings, enhanced reputation as an inclusive organisation, and ability to attract top talent, loyal customers, and investors, driving business growth and competitive advantage.
The Importance Of Diverse Suppliers Within The Supply Chain
In today’s globalised world, businesses face the challenge of managing transparent supply chains while meeting consumer expectations for diversity, sustainability, and ethics. Embracing supplier diversity—sourcing from minorities, women, veterans, LGBTQ+ individuals and other underrepresented groups—addresses this challenge and offers substantial benefits.
This strategy drives innovation, builds resilience, and opens new markets. It’s more than a moral responsibility; it’s a key tactical decision. By incorporating diverse suppliers, companies enhance competitiveness, foster growth, and contribute positively to local economies, aligning business success with corporate social responsibility.
The Strategic Importance of Diverse Suppliers
Fostering Innovation
Diverse suppliers bring fresh perspectives and unique ideas that can ignite innovation. These new viewpoints help businesses develop groundbreaking products, enhance services, and improve processes. Fusing diverse thoughts can lead to creative solutions, giving companies a competitive edge.
Google, for instance, collaborates with diverse small businesses to connect minorities, women, LGBTQ+, disabled individuals, and veterans with business opportunities, fostering innovation in their supply chain. By outsourcing areas they don’t cover—like food and transportation—Google encourages information sharing and innovation, as these companies frequently use Google products and provide valuable feedback for improvement.
Enhancing Market Insight
Diverse suppliers often possess deep knowledge of various niche markets. By collaborating with these suppliers, businesses gain valuable insights into different consumer segments. This understanding allows companies to tailor their offerings to meet diverse needs, expanding their market reach and increasing profitability.
Driving Positive Social Impact
Supporting diverse suppliers promotes economic growth in underrepresented communities and fosters social equality. This commitment to social responsibility enhances a company’s reputation and aligns with consumer values as more people seek to support businesses prioritising ethical and inclusive practices.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Many governments and large corporations have policies that encourage or mandate supplier diversity. By incorporating diverse suppliers, businesses can ensure compliance with these regulations, avoid penalties, and access new contracts and opportunities. This compliance protects the company and can drive growth through new business avenues.
What Supply Chain Diversity Brings to Your Business
Different suppliers bring fresh ideas, new ideas and unique solutions to your business. Tapping into different customer segments and niche markets broadens your market reach. Diversified suppliers also increase flexibility by reducing reliance on a single source, reducing disruption risks.
Dealing with diverse suppliers demonstrates your commitment to social responsibility, enhances your brand and attracts loyal customers. Complying with regulations and finding new opportunities further strengthens your competitive advantage. Ultimately, diversification helps drive innovation and growth and sets your business apart in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Challenges of Supply Chain Diversity
Here are the top 5 challenges to supply chain diversity, presented concisely:
- Identifying Qualified diversified suppliers – Finding and analysing suitable diversified suppliers, especially in industries or sectors with limited product diversity.
- Addressing systemic barriers – Diverse suppliers often face systemic barriers, such as capital, network infrastructure, and limited resources.
- Ensuring Supplier Capabilities – There are concerns about the ability of diverse suppliers to meet quality, supply, and performance standards.
- Creating cultural change – The challenge of promoting a mindset shift and cultural change in organisational and supply chain ecosystems.
- Accurate data and measurement – Challenges in tracking and measuring diversity metrics across multiple tiers of suppliers.
Conclusion
Supply chain diversity propels innovation, resilience, and competitiveness. Embracing diversity offers new markets, ideas and partnerships. Committed leadership and an inclusive culture overcome the challenge of reaping the benefits of diversity – enhanced reputation, talent magnetism and business growth. Ultimately, it supports morale while creating a more equitable and sustainable working environment.
Key Takeaways
- Supply chain diversity involves intentionally engaging diverse suppliers from underrepresented groups.
- Requires commitment to representation, meaningful change, diverse perspectives, transparency, and proactive outreach.
- Implementation strategies include formal programs, goals, collaboration, inclusive policies, capacity building, and metrics tracking.
- Challenges include identifying suppliers, overcoming barriers, ensuring capabilities, driving cultural change, and accurate measurement.
FAQs
How does supply chain diversity contribute to competitive advantage?
It enables access to new markets and customer segments, fosters innovation, enhances brand reputation, improves operational resilience through risk diversification, and supports talent attraction and retention by promoting an inclusive culture.
What metrics can be used to measure supply chain diversity?
Common metrics include the number of diverse suppliers, spending with them, the percentage of diverse suppliers in different product/service categories, and performance evaluations.
